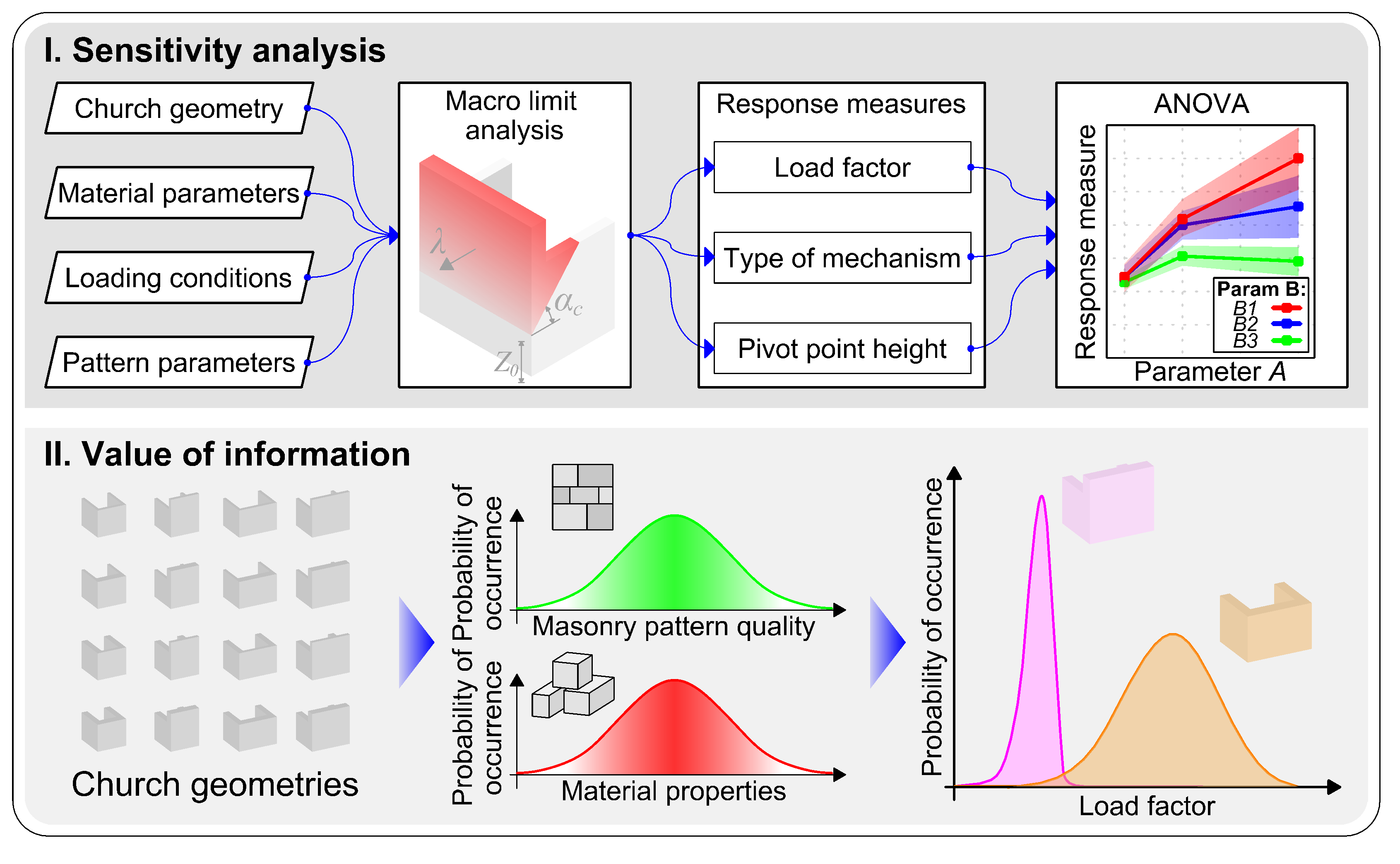
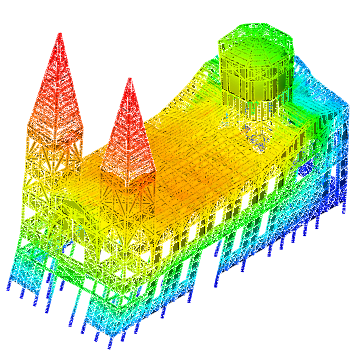
A two-step strategy for the mechanical analysis of unreinforced masonry (URM) structures, either subjected to in- or out-of-plane loading, is presented. At a first step, a semi-automatic digital tool allows the parametric modelling of the structure that, together with an Upper bound limit analysis tool and a heuristic optimisation solver, enables tracking the most prone failure mechanism. At a second step, a coupled concurrent FE model with micro- and macro-scales is assumed. A micro-modelling description of the masonry is allocated to regions within the failure mechanism found in the former step. In converse, the other domain regions are modelled via a macro-approach, whose constitutive response is elastic and orthotropic and formulated through closed-form homogenized-based solutions. The application of the framework is based on non-linear static (pushover) analysis and conducted on three benchmarks: (i) an in-plane loaded URM shear wall; (ii) a U-shaped URM structure; and (iii) a URM church. Results are given in terms of load capacity curves, total displacement fields, and computational running time; and compared against those found with a FE microscopic model and with a limit analysis tool. Lastly, conclusions on the potential of the framework and future research streams are addressed.